Coding 101: Coding Quick Start
1.0 Intro
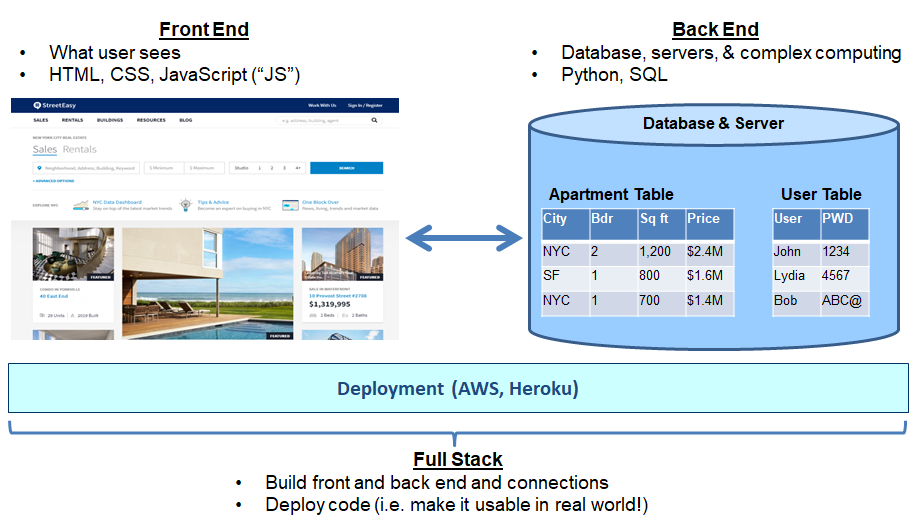
Coding 100 Level Courses: Full Stack Web Development & Deployment
What is full stack web development? It let’s you build and deploy websites!!
101: Front end web development overview
Front End
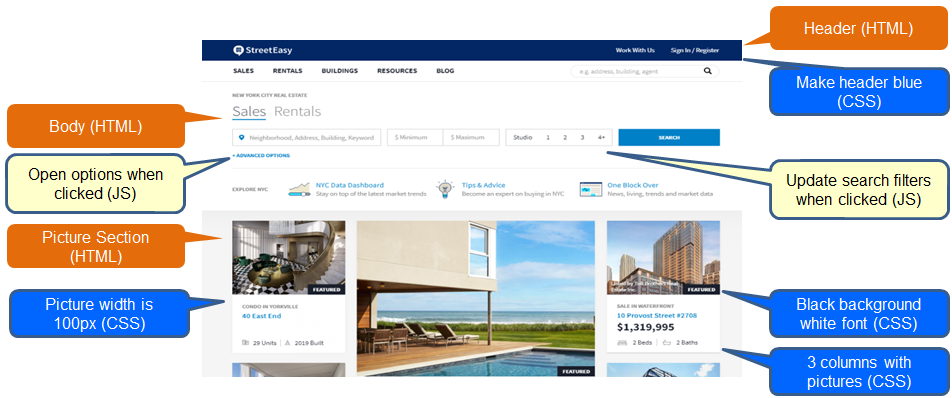
- HTML gives website basic skeletal structure, written text, pictures, and links (like your bones)
- CSS makes site look good through formatting (like your skin and make-up)
- JavaScript provides site with functionality and computation ability (like your muscles)
Lesson Overview
- Google Chrome inspector tool
- User input / output with alert() and prompt()
- Storing data in variables
- Strings vs. Numbers and the ParseInt() function
- If then else statements
- Comments
- Random number generators
- MS Visual Studio Code
- Running JS files locally
Project Overview
- Hello World – Learn the first program typically made in any new language that you are learning. Tell user hello world
- Greet User – Ask for the user’s name and then greet them.
- Tip Calculator – Ask user for bill amount and what percentage they would like to tip. Tell them the tip amount in dollars and the total bill.
- ID Checker – Ask for you users birth date and let them drink if they are over 21.
- Multiplication Quiz – Create a fun quiz to test your mental math skills.
Coding 101: Coding Quick Start
1.1 Google Inspector Tool
Download Google Chrome (https://www.google.com/chrome/)
Use insepctor tool
- Open any website page with Google Chrome
- Right click and press inspect
- Click on “Console”
Coding 101: Coding Quick Start
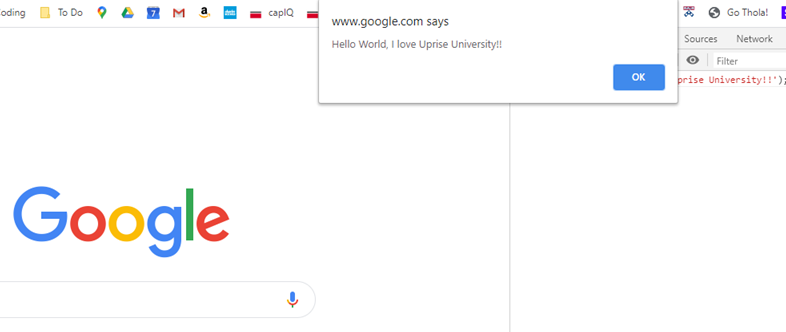
1.2 User input / output with alert() and prompt()
Google Chrome Inspector Tool and your first project: 1.1 Hello World
alert('hello world, I love Uprise University')
Coding 101: Coding Quick Start
1.3 Storing data in variables
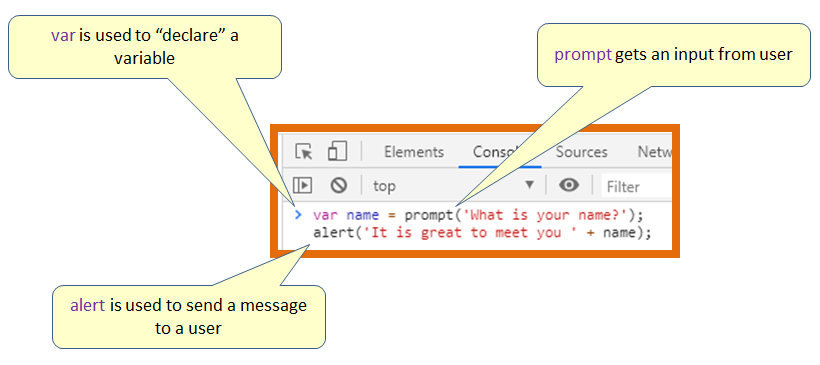
Project 1.2: Greet User
This code prompts the user to fill in their name
Then it “declares” a variable called “name” and stores that user input into it
It then sends an alert message to the user using the information stored in the variable “name”
Notes - Press shift and return to type in the second line of code without running the first; then press enter to run the code
Coding 101: Coding Quick Start
1.4 Strings vs. Numbers and the ParseInt() function
“Strings” are words, letters, and characters that you would type into a keyboard
Numbers are the ten digits that you can type into a keyboard
If the number has decimals, then it is called a “Float”; if it doesn’t, then it is called an “Integer”
When you add to numbers together, you get the sum total of those two numbers, for example: 2+ 3 --> 5
When you add two strings together, however, it “Concatenates” them; (i.e. puts them together) For example, ‘2’+’3’ --> ’23’
To convert a string into a number, you must use the parseInt() method
For example, parseInt(‘2’) + parseInt(‘3’) --> 5
Note that parseInt () is case sensitive!
parseInt() can be helpful when you want to convert user input into a number
Project 1.3: Tip Calculator
Try to create this program yourself first before looking at the answer
Create a program that calculates the tip you need to pay at a restaurant
Ask user how much the bill was and how much they want to tip
Tell the user how much to tip and what the total bill is going to be
Remember to use
- alert()
- prompt()
- parseInt()
- var x = 2020 – age;

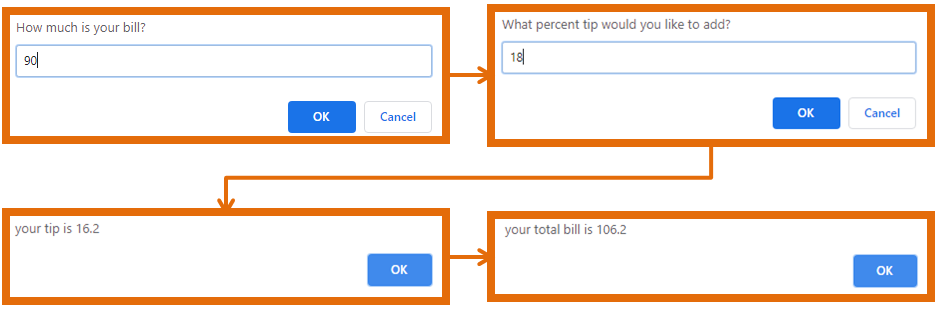
Tip Calculator Prompt
Tip Calculator Answer
Coding 101: Coding Quick Start
1.5 If then else statements
If then else statements create the basic logic in your program
It reads: if something is true then do some tasks, else, if it is not true, do some other tasks

Note that each line that is doing something has a semicolon after it but not the lines with the if or else
One of the most annoying things about coding is that computers are very literal and programs don’t work if you are missing a semi-colon, a letter that is supposed to be lower case is uppercase, etc.!! This can cost you hours of time and lots of frustration so pay attention to the details and the “syntax” of the code!!
We will also show you how to use programs, like MS Visual Studio Code, that help you “debug” and avoid making these types of mistakes (because they can be REALLY annoying to find!)
Also note that you don’t actually have to write out “then”, you simply use the curly brackets before and after the block of code that you want to run when the statement is true
Project 1.4: ID Checker
Try to create this program yourself first before looking at the answer
Create a program that asks the user what year they were born
It then checks to see if the user is 21
If they are 21 or older, the program tells the user that they can drink, otherwise it says that they can’t
For simplicity, just assume the current year is constant and disregard the month and day that they were born. For example, someone born in 1990 is 30 years old (i.e. 2020-1990)
Remember to use
- alert()
- prompt()
- parseInt()
- if () { } else { }
- var x = 2020 – age;
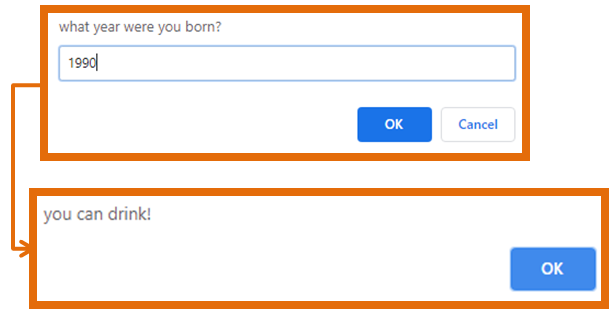
ID Checker Project Prompt
ID Checker Project Answer
Coding 101: Coding Quick Start
1.6 Comments
Comments are notes that you can use to help you or other programmers looking at your code remember what the code does
The program does not actually do anything with this code

Coding 101: Coding Quick Start
1.7 Random number generators
It is often useful to generate random numbers
The function Math.random() returns a random number between 0 and 1
The function Math.floor() returns the largest integer less than or equal to a given number
Combining them and multiplying the random number by 10 will get you a random between 0 and 9
Math.floor(Math.random()* 10)
You can multiply it by 10 and add 1 to get a random number between 1 and 10 or multiply it by 100 and add 1, to get a number between 1 and 100
You can also multiply it by 10 and add 1 to get a random number between 1 and 10, and then multiply the result of Math.floor() by 10 again to get a random number between 10 and 100 that is a multiple of 10…tricky, we know!!!
Note: These types of tricks are very useful in coding because it safes you a lot of time and lines of code. Coding is all about efficiency and little tricks! So remember to look for them!
Project 1.5: Multiplication quiz
Create a math quiz that asks the user to multiply two random numbers together
If the user gets the right answer, then alert the user that they got it right, otherwise alert them that they got it wrong
To make the exercise a little trickier, make the first random number an integer between 1 and 100 and the second random number an integer between 10 and 100 that is a multiple of 10!
Remember to use

Multiplication Quiz Project Prompt
Multiplication Quiz Project Answer
Coding 101: Coding Quick Start
1.8 MS Visual Studio Code
Download and Use MS Visual Studio Code for previous exercises
This will allow you to store files of code easily
It is color coordinated so that it is easier to read your code
It is free!

There are lots of other code editors out there though so feel free to use whichever one you prefer

Download and Use MS Visual Studio Code for previous exercises
Set-up
Link Download Microsoft VS Code
https://code.visualstudio.com/downloadCoding 101: Coding Quick Start
1.9 Running JS files locally
Step 1) Create 1 HTML file and 1 JavaScript file
- index.js
- playground.html
Step 2) Link your html file to your JavaScript file so that it runs when you open HTML file; Write this in your HTML code
script src=index.js> script>
Step 3) Write you code in JavaScript file
alert(‘Hello World’);
Step 4) Go to the html file and open it with Google chrome
Always make sure to save all files before running program
Note, to open file in Chrome, you should be able to just double click the file or right click the file and then click “open with” and then google chrome
Homework Assignments to do before next lesson
Create the following programs
- Days alive : Ask a user how old they are and then tell them how many days they have lived
- Temp converter: App converts temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit or vice versa
- Vowel? Ask user to enter a letter. Tell user if it is a vowel or not